Detailed Description: Knee Arthroscopy
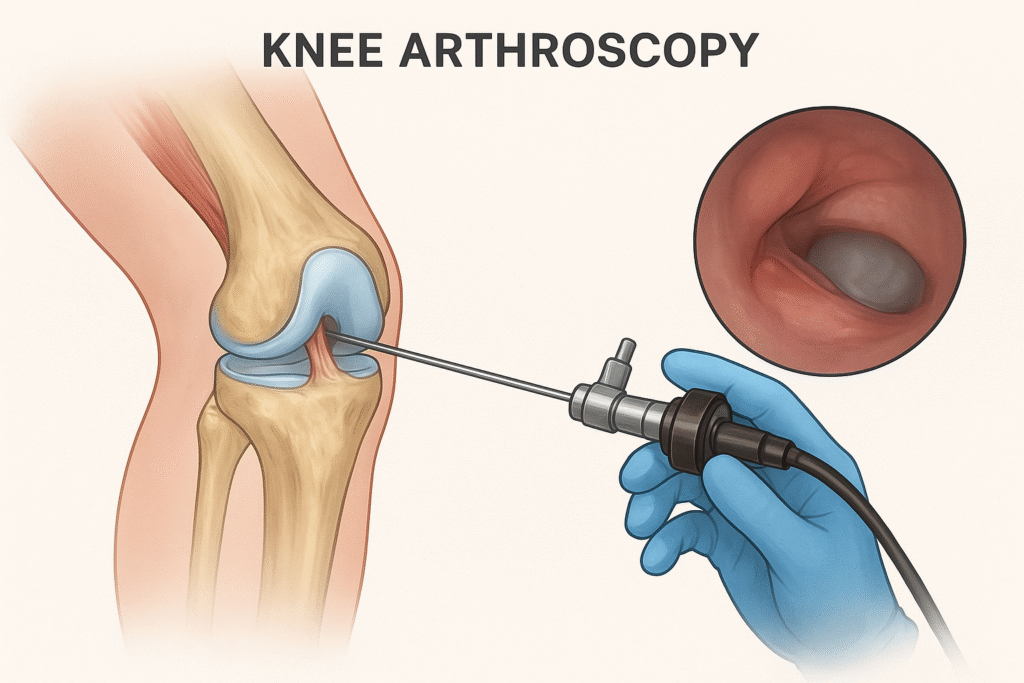
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting the knee joint. Instead of making a large incision, the surgeon makes two or three small cuts and inserts an arthroscope—a thin tube with a camera and light—into the knee. This camera projects a clear, magnified view of the joint onto a monitor, allowing the surgeon to see structures inside the knee such as cartilage, ligaments, and the meniscus.
Using additional small instruments inserted through the other incisions, the surgeon can repair or remove damaged tissues, smooth rough cartilage, or reconstruct torn ligaments. Because the procedure is minimally invasive, it causes less trauma to tissues compared to traditional open surgery.
Common Conditions Treated with Knee Arthroscopy
- Meniscus tears
- ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) and PCL injuries
- Loose bone or cartilage fragments
- Synovitis (inflammation of knee lining)
- Patellar (kneecap) problems
- Cartilage damage due to injury or early arthritis
Procedure Steps
- Anesthesia is administered (local, regional, or general).
- Small incisions are made around the knee.
- Arthroscope insertion allows internal viewing on a video screen.
- Miniature tools are used to repair or remove damaged tissue.
- Incisions are closed with small stitches or adhesive strips.
Benefits of Knee Arthroscopy
- Minimally invasive with small incisions
- Reduced pain and swelling after surgery
- Faster rehabilitation and quicker return to routine activities
- Lower risk of complications
- Less scarring
Recovery
Patients often go home the same day and begin gentle movement soon after surgery. Physiotherapy plays a key role in strengthening the knee and restoring mobility. Most people return to normal activities within a few weeks, depending on the procedure performed.
Summary
Knee arthroscopy is a safe, effective, and advanced surgical method widely used to treat knee injuries and joint problems. By enabling precise diagnosis and treatment through tiny incisions, it enhances patient outcomes with shorter recovery times and minimal discomfort.
