Detailed Description: Ligament Injury
A ligament injury occurs when one of the strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that connect bones at a joint is stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. Ligaments play a crucial role in stabilizing joints and guiding normal movement. When they are injured due to trauma or excessive strain, joint stability and function are compromised.
Causes of Ligament Injuries
Ligament injuries commonly happen due to:
- Sudden twisting or pivoting motions
- High-impact sports activities (e.g., football, basketball, skiing)
- Falls, accidents, or direct blows
- Overstretching or repetitive stress
- Improper landing from a jump
Common Types of Ligament Injuries
Although ligament injuries can occur in many joints, they most frequently affect:
- Knee ligaments – e.g., ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament), PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament), MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament), LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament)
- Ankle ligaments – commonly injured during twisting or rolling of the ankle
- Shoulder and wrist ligaments – injury occurs due to falls or sudden pulling forces
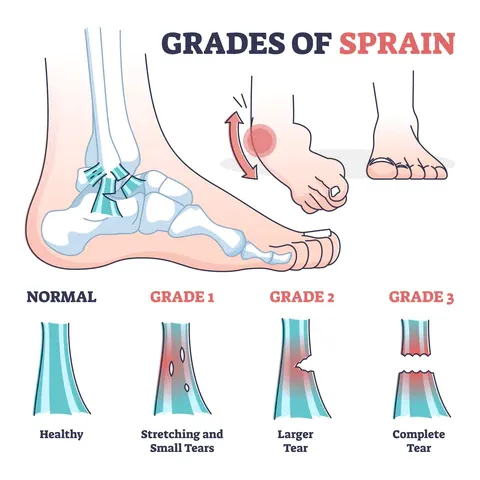
Ligament injuries are classified by severity into grades:
- Grade 1: Mild stretching and microscopic tears
- Grade 2: Partial tear with noticeable looseness
- Grade 3: Complete rupture causing significant joint instability
Symptoms
- Sudden sharp pain at the time of injury
- Swelling and inflammation
- Bruising or discoloration
- Joint instability or feeling of “giving way”
- Limited range of movement
- Difficulty bearing weight on the affected limb
Diagnosis
Doctors typically diagnose ligament injuries by:
- Physical examination
- Stress tests to assess stability
- Imaging procedures such as X-ray (to rule out fractures), MRI (to evaluate soft tissue damage), or ultrasound
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity and location of the injury:
Non-surgical Options
- RICE Protocol: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
- Pain-relief medications and anti-inflammatory drugs
- Bracing or supports
- Physiotherapy to restore strength and mobility
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be required for complete tears or when instability affects daily function. Common procedures include:
- Ligament repair
- Ligament reconstruction (often using tendon grafts, e.g., for ACL tears)
Recovery & Rehabilitation
Recovery time varies depending on the severity:
- Mild injuries: 2–6 weeks
- Moderate injuries: 2–3 months
- Severe or surgically treated injuries: 6–12 months
Rehabilitation focuses on:
- Reducing pain and swelling
- Restoring strength and flexibility
- Preventing future injuries
- Gradual return to sports or work activities
Summary
Ligament injuries are common, especially in athletes and active individuals. Early diagnosis and proper treatment—whether conservative or surgical—are essential for restoring joint stability, preventing long-term complications, and enabling a safe return to activity
KNEE LIGAMENT IMAGE
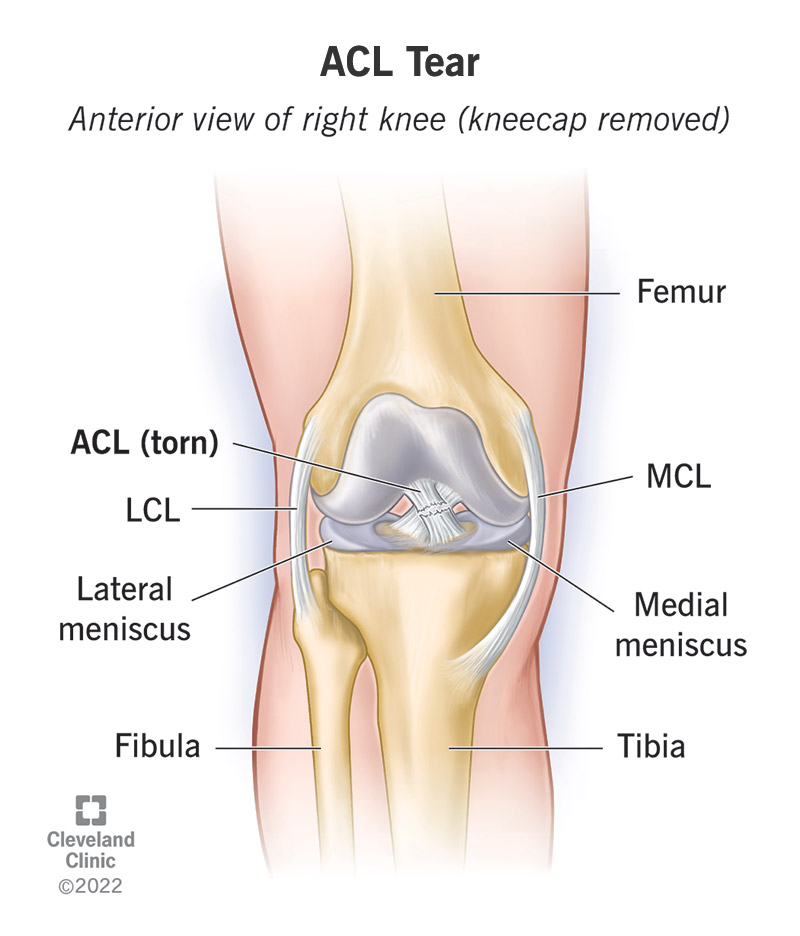
IMAGE-2