Here is a detailed description about CTEV (Clubfoot):
CTEV – Congenital Talipes Equinovarus
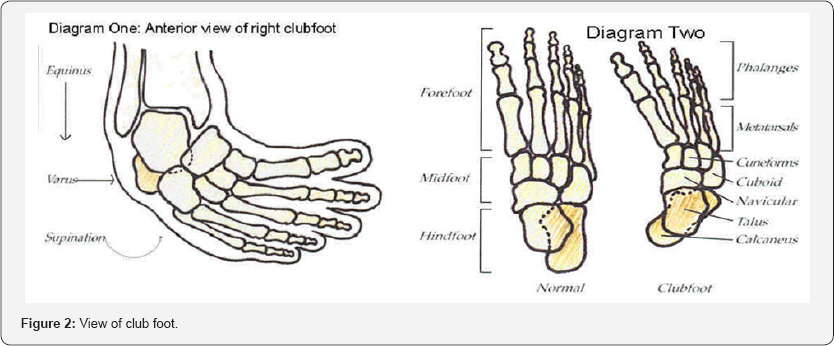
CTEV, commonly known as Clubfoot, is a congenital deformity of the foot and ankle in which one or both feet are twisted inward and downward. It is present at birth and is one of the most common pediatric orthopedic conditions.
Meaning of CTEV
- C – Congenital → Present at birth
- T – Talipes → Related to ankle and foot
- E – Equinus → Foot pointing downward (like standing on toes)
- V – Varus → Heel turned inward (foot curved inward)
So, the foot appears inward-turned and toe-downward — giving a club-shaped appearance.
Types of Clubfoot (CTEV)
1. Idiopathic (Most common)
- Occurs without any other medical condition
- Usually seen in otherwise healthy babies
2. Syndromic
- Associated with neuromuscular disorders (e.g., spina bifida, arthrogryposis)
3. Postural
- Due to abnormal positioning in the womb, usually flexible and easily correctable
Causes / Risk Factors
The exact cause is unknown, but possible factors include:
- Genetic influence (family history)
- Intrauterine position
- Neurological or muscular imbalance
- Connective tissue or bone development issues
- Associated syndromes
More common in:
- Males (2:1 ratio)
- First-born babies
- When there is less amniotic fluid
Clinical Features
- Foot is twisted inward and downward
- Calf muscle appears smaller
- Foot size may be shorter
- Limited ability to move foot upward or outward
- Often affects both feet (bilateral) in 50% of cases
- Painless at birth
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination immediately after birth
- Prenatal diagnosis possible via ultrasound after 20 weeks gestation
- X-ray rarely needed in newborns
Treatment
Ponseti Method (Gold Standard Treatment)
Most popular and effective, with 95% success rate.
Steps:
- Serial Manipulation & Casting (weekly cast changes for 5–6 weeks)
- Tenotomy (Achilles tendon release) if needed to correct equinus deformity
- Foot Abduction Brace (FAB) to prevent recurrence
- 23 hours/day for 3 months
- Night-time only until age 4–5 years
Other options
- French functional physiotherapy method
- Surgical release (for resistant or relapsed cases)
Goals of treatment
- Straight, pain-free, fully functional and plantigrade foot
- Ability to walk, run and play normally
- Prevent long-term disability and deformity
Complications if untreated
- Difficulty walking
- Permanent deformity
- Callus formation
- Leg length difference
- Social and psychological impact
Summary Table
| Feature | Description |
| Full Form | Congenital Talipes Equinovarus |
| Type | Congenital foot deformity |
| Appearance | Foot turned inward & downward |
| Treatment | Ponseti method with braces |
| Outcome | Excellent with early management |
Image-1
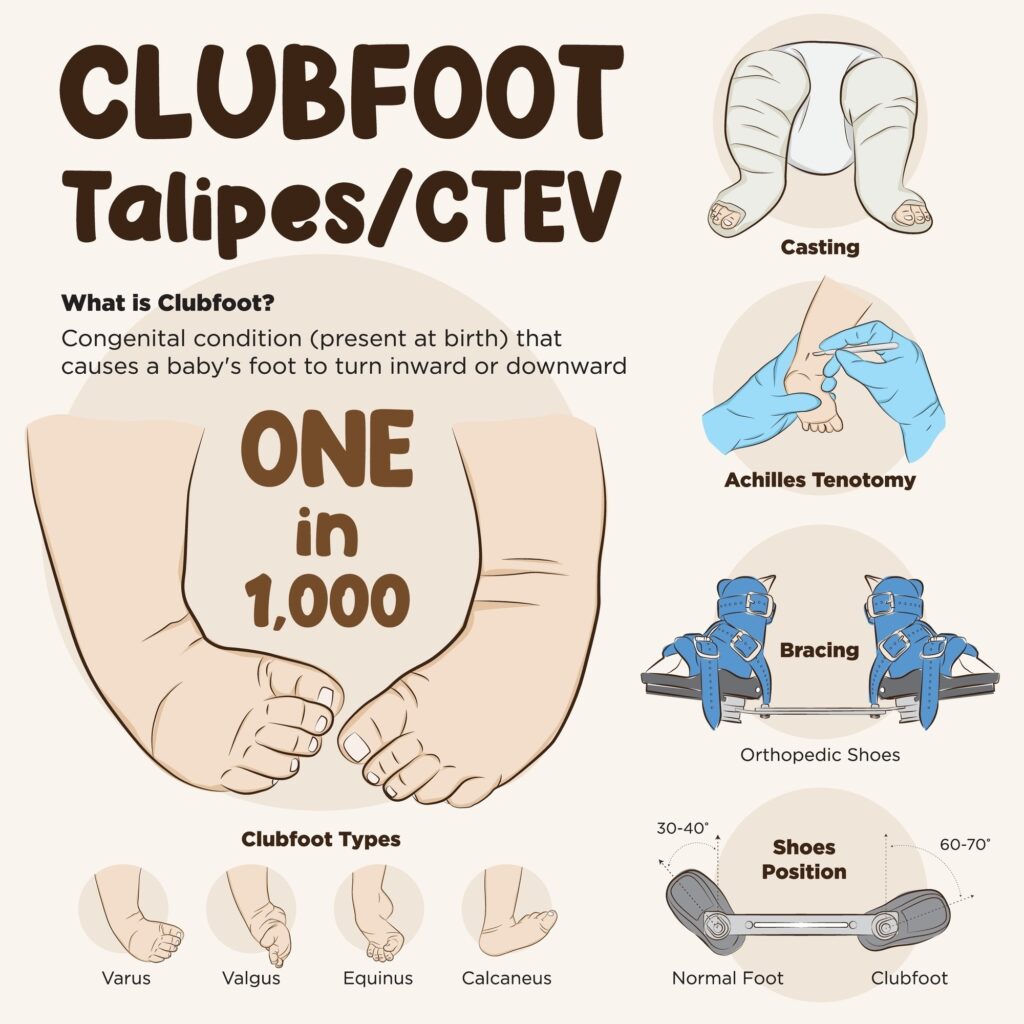
Image-2